Wireless Networks in Integrated IT and OT Systems – Module 3 Exam Answers
In today’s increasingly connected world, the integration of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) systems has become critical for industries striving for greater efficiency, automation, and real-time decision-making. Wireless networks, as a key enabler, facilitate the seamless communication between these two systems. This essay will explore the role of wireless networks in integrated IT and OT systems, their benefits, challenges, and how they shape modern industrial environments.
1. What is the main difference between licensed and unlicensed spectrums in wireless communications?
- Licensed spectrums are for exclusive use by specific mobile network operators, while unlicensed spectrums requires permission from the FCC.
- Licensed spectrums are purchased for exclusive use by specific mobile network operators, while unlicensed spectrums are for non-exclusive use without needing permission from the FCC.
- Licensed spectrums are available for non-exclusive use, while unlicensed spectrums are purchased for exclusive use by specific mobile network operators.
- Licensed spectrums are for non-exclusive use, while unlicensed spectrums requires a licensing fee for exclusive use.
Licensed spectrums are allocated exclusively to specific mobile network operators or individual companies that pay a licensing fee for the right to transmit on an assigned frequency within a specific geographic area.
The correct answer is:
Licensed spectrums are purchased for exclusive use by specific mobile network operators, while unlicensed spectrums are for non-exclusive use without needing permission from the FCC.
Explanation:
- Licensed Spectrum:
- Allocated to specific mobile network operators or entities.
- Requires payment of a licensing fee and compliance with regulatory guidelines.
- Exclusive use within a defined geographic area and frequency band, minimizing interference.
- Unlicensed Spectrum:
- Open for non-exclusive use by anyone without requiring a license.
- Governed by general rules set by the FCC (or equivalent regulatory body).
- Commonly used by technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and IoT devices, often prone to more interference.
2. Which wireless technology is commonly used in home automation for lighting controls, security, and HVAC systems, as well as in healthcare settings for Medical Body Area Network Systems (WBANS)?
- Zigbee
- Bluetooth
- NFC (Near Field Communication)
- IrDA (Infrared Data Association)
Zigbee is a wireless technology commonly used in home automation for various applications, including lighting controls, security systems, and HVAC systems. Additionally, Zigbee is utilized in healthcare settings for Medical Body Area Network Systems (WBANS) that can monitor vital signs such as heart rate and blood pressure and medication adherence. Zigbee operates as part of Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs), providing low-power and short-range wireless communication within a relatively small area.
The correct answer is:
Zigbee
Explanation:
Zigbee is a wireless technology commonly used in:
- Home Automation: Lighting controls, security systems, HVAC systems, and other smart home devices.
- Healthcare Settings: Used in Medical Body Area Network Systems (WBANS) to monitor vital signs (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure) and track medication adherence.
Key Features of Zigbee:
- Operates as part of Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs).
- Provides low-power and short-range communication, ideal for battery-powered devices.
- Offers reliability, scalability, and low latency, making it suitable for both smart home and medical applications.
3. Which IEEE standard is commonly used as the basis for Wi-Fi, the most common Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) technology?
- IEEE 802.15
- IEEE 802.3
- IEEE 802.16
- IEEE 802.11
Wi-Fi, the most common Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) technology, is based on the IEEE 802.11 wireless standards. These standards define the protocols for implementing WLAN communication, allowing devices to connect and communicate over short distances. Using IEEE 802.11 standards ensures interoperability and compatibility among various Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
The correct answer is:
IEEE 802.11
Explanation:
Wi-Fi, the most common Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) technology, is based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. These standards:
- Define the protocols and specifications for wireless communication in WLANs.
- Enable devices to connect and communicate over short to medium distances.
- Ensure interoperability and compatibility among Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
Key Features of IEEE 802.11:
- Supports various versions (e.g., 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax) to enhance speed, range, and performance over time.
- Widely used in homes, businesses, and public spaces for wireless internet access.
4. Which wireless technologies are commonly utilized for providing internet broadband connectivity globally through public cellular networks in Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs)?
- Bluetooth and NFC
- 4G, 5G, and LTE
- Wi-Fi and Zigbee
- IEEE 802.11 and IEEE 802.16
Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) provide connectivity across large geographic regions beyond the range of WLANs and WMANs. They enable internet broadband connectivity globally through public cellular networks such as 4G (Fourth Generation), 5G (Fifth Generation), and LTE (Long-Term Evolution).
he correct answer is:
4G, 5G, and LTE
Explanation:
Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) use public cellular networks to provide internet broadband connectivity over large geographic regions. Technologies like 4G, 5G, and LTE are commonly used in WWANs for:
- Global Connectivity: Enabling high-speed internet access across countries and continents.
- Wide Coverage: Extending connectivity beyond the range of Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (WMANs).
- Applications: Mobile internet, IoT (Internet of Things), smart cities, and more.
These cellular technologies are essential for modern mobile broadband and support high data rates, low latency, and reliable connectivity.
5. What is a key characteristic of Wi-Fi 6E that makes it well-suited for industrial environments?
- Wi-Fi 6E is primarily designed for non-critical sensing applications.
- Wi-Fi 6E is backward compatible with previous Wi-Fi standards.
- Wi-Fi 6E operates in the 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz frequency bands.
- Wi-Fi 6E provides an interference-free spectrum in the 6-GHz band.
Wi-Fi 6E operates in the 6-GHz radio-frequency band, providing an interference-free spectrum that allows for much faster speeds and has no signal interference from 2.4-GHz and 5-GHz Wi-Fi networks. This characteristic makes Wi-Fi 6E well-suited for industrial environments where reliable low-latency communications, high throughput, and increased device density are essential.
The correct answer is:
Wi-Fi 6E provides an interference-free spectrum in the 6-GHz band.
Explanation:
Wi-Fi 6E extends Wi-Fi 6 capabilities into the 6-GHz frequency band, offering:
- Interference-Free Spectrum: The 6-GHz band is not congested with legacy Wi-Fi traffic from 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, reducing interference.
- High Throughput and Low Latency: Ideal for industrial environments where critical operations rely on fast and reliable communication.
- Support for Increased Device Density: Efficiently handles a large number of connected devices, essential in industrial and IoT-heavy setups.
This makes Wi-Fi 6E particularly well-suited for industrial environments, ensuring robust and reliable communication for applications like automation, monitoring, and real-time control systems.
6. In addition to the manufacturing sector, which industry verticals are applying private 5G technology for various applications and use cases?
- Telecommunications, agriculture, and mining
- Agriculture, healthcare, and retail
- Agriculture, transport and logistics, mining, healthcare, and oil and gas
- Retail, education, and telecommunications
In addition to the manufacturing sector, other industry verticals are applying private 5G technology for various applications and use cases, including agriculture, transport and logistics, mining, healthcare, and oil and gas. Private 5G technology is being utilized across various sectors to enable wireless connectivity for industrial equipment, automated/autonomous vehicles, sensors and inspection systems, and location services with accurate tracking of assets and personnel.
The correct answer is:
Agriculture, transport and logistics, mining, healthcare, and oil and gas
Explanation:
Private 5G technology is increasingly being adopted in a variety of industries beyond manufacturing to enable advanced wireless connectivity. These sectors include:
- Agriculture: Supports precision farming, IoT-enabled sensors for crop monitoring, and autonomous farming equipment.
- Transport and Logistics: Enhances supply chain management, real-time tracking, and automation in warehouses and ports.
- Mining: Enables autonomous vehicles, safety monitoring, and real-time communication in remote locations.
- Healthcare: Facilitates telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and connected medical devices.
- Oil and Gas: Provides reliable communication in remote locations, enables IoT-based monitoring of equipment, and ensures worker safety.
Private 5G networks are valued for their low latency, high reliability, large device capacity, and enhanced security, making them a key enabler across diverse use cases.
7. Which of the following is NOT one of the main components of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) sensor nodes?
- Display screen
- Power supply (battery)
- Memory
- Sensors and actuators
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) sensor nodes typically have five main components: memory, sensors and actuators, a power supply (battery), a microcontroller or processor, and a communication device such as a radio transceiver. However, a display screen is not a standard component of WSN sensor nodes. These nodes are designed to collect data from the environment, process it, and wirelessly transmit the information to other nodes or sink nodes. The data is then forwarded to a gateway for connection to external networks or the Internet. Display screens are more commonly found in devices designed for user interaction, which is not the primary function of WSN sensor nodes.
The correct answer is:
Display screen
Explanation:
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) sensor nodes are typically designed for efficient sensing, processing, and communication. Their main components include:
- Power supply (battery): Provides energy for the node’s operation.
- Memory: Stores data and program instructions.
- Sensors and actuators: Capture environmental data and, optionally, perform actions based on it.
- Microcontroller/processor: Processes data and manages node operations.
- Communication device: Enables wireless transmission of data.
A display screen is not a standard component of WSN sensor nodes, as these devices are not designed for direct user interaction. Instead, their primary purpose is to gather, process, and transmit data wirelessly within the network.
8. Which statement accurately describes a characteristic of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs)?
- Sensor nodes in WSNs are typically deployed in a specific topology.
- WSNs are deployed with detailed planning to ensure optimal coverage.
- WSNs are typically powered by a constant and reliable power source.
- WSNs consist of many sensor nodes densely deployed over a geographical area, often powered by limited-capacity batteries.
WSNs typically consist of many sensor nodes densely deployed over a geographical area. Batteries with limited power capacity usually power these sensor nodes. Changing batteries in a node is often difficult or impossible, making them disposable. Additionally, WSNs are characterized by ad hoc deployment without detailed planning, and the sensor nodes must organize themselves into a communication network. The topology of a WSN may change frequently due to sensor node failures and movement. These unique characteristics set WSNs apart from traditional wireless networks.
The correct answer is:
WSNs consist of many sensor nodes densely deployed over a geographical area, often powered by limited-capacity batteries.
Explanation:
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have the following characteristics:
- Dense Deployment: Many sensor nodes are deployed across a geographic area to monitor environmental conditions or specific parameters.
- Limited Power Capacity: Sensor nodes are usually powered by small batteries, which are challenging or impossible to replace in many deployments, leading to power-conservation considerations.
- Ad Hoc Deployment: WSNs are often deployed without detailed planning, and the nodes self-organize into a communication network.
- Dynamic Topology: Node failures, energy depletion, or environmental factors can cause frequent changes in the network’s topology.
These features make WSNs suitable for applications like environmental monitoring, disaster response, and industrial automation, where flexibility and scalability are crucial.
9. In Packet Tracer, what is the purpose of the Config tab when configuring intermediate devices like routers and switches?
- To access the Command Line Interface (CLI)
- To simulate the functionality of a device
- To provide a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for configuration
- To export device configuration files
The Config tab in Packet Tracer serves as a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for configuring intermediate devices like routers and switches. It is not meant to simulate the functionality of a device but rather provides a visual interface for users who may need to become more familiar with the Command Line Interface (CLI). As settings are changed in the GUI, the equivalent CLI commands appear in the Equivalent IOS Commands window, facilitating the learning of CLI commands and the Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS). The Config tab is unique to Packet Tracer and allows users to configure basic settings using a visual interface.
The correct answer is:
To provide a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for configuration
Explanation:
The Config tab in Cisco Packet Tracer offers a Graphical User Interface (GUI) that allows users to configure intermediate devices like routers and switches without using the Command Line Interface (CLI).
Key characteristics of the Config tab:
- Ease of Use: Designed for users who may not be familiar with CLI, enabling basic device configuration through a visual interface.
- Learning Aid: Displays the equivalent CLI commands in the “Equivalent IOS Commands” window, helping users learn how to perform the same configurations in CLI.
- Basic Configuration: Allows setting up essential parameters like interfaces, IP addresses, and routing protocols.
- Simulation Support: Facilitates easier configuration in simulation environments like Packet Tracer.
This feature is specific to Packet Tracer and is particularly helpful for beginners in networking.
10. In Packet Tracer, what feature provides a desktop interface for some end devices, such as PCs and laptops, offering access to apps like IP configuration, wireless configuration, a command prompt, and a web browser?
- Desktop Tab
- Desktop Simulator
- Device Manager
- Configuration Manager
Packet Tracer’s Desktop Tab feature provides a desktop interface for certain end devices like PCs and laptops. This interface includes a set of apps that allow users to perform tasks such as IP configuration, wireless configuration, access a command prompt, and use a web browser. The Desktop Tab simulates the functionalities of a desktop environment, providing a comprehensive experience for end device configurations and interactions.
The correct answer is:
Desktop Tab
Explanation:
In Packet Tracer, the Desktop Tab is a feature available on certain end devices, like PCs and laptops, which provides access to a simulated desktop interface. This tab includes applications and tools for configuration and testing, such as:
- IP Configuration: Allows users to assign static IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways or configure DHCP.
- Wireless Configuration: Enables setup and management of wireless network settings.
- Command Prompt: Simulates a terminal interface for testing connectivity using commands like
ping,tracert, and more. - Web Browser: Simulates internet browsing to test HTTP/HTTPS connections in a network.
The Desktop Tab enhances learning by allowing users to interact with end devices as they would in a real-world scenario, testing connectivity and configurations within the network simulation.
11. Which feature of Bluetooth 5 addresses the challenge of interference with other wireless networks like Zigbee and Wi-Fi?
- Extended range to 50m
- Increased speed to 2mbps
- Mesh topology
- Beaconing
Beaconing is the feature of Bluetooth 5 that addresses the challenge of interference with other wireless networks like Zigbee and Wi-Fi. Beaconing allows factory floor personnel to receive information from locally placed transmitters with their cellphones. This feature facilitates efficient communication in environments where multiple wireless protocols coexist, helping to reduce interference and improve overall performance.
The correct answer is:
Beaconing
Explanation:
Beaconing is a feature of Bluetooth 5 that helps address interference challenges in environments where multiple wireless networks (e.g., Zigbee, Wi-Fi) coexist. Here’s how it works:
- Efficient Communication: Beaconing enables Bluetooth devices to broadcast data packets in a way that minimizes interference with other networks.
- Localized Information Sharing: It allows devices like smartphones or sensors to receive information from nearby transmitters, such as location-specific updates on a factory floor.
- Improved Coexistence: Beaconing uses adaptive frequency hopping and efficient broadcasting techniques to reduce the likelihood of interference with other wireless technologies operating in the same frequency bands.
This feature is particularly useful in environments with dense wireless device usage, ensuring smooth operation and reliable communication.
12. Which layer of the OSI model is covered by IEEE 802.15.4?
- Network Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Transport Layer
- Application Layer
IEEE 802.15.4 covers the Data Link Layer of the OSI model. The Data Link Layer provides access to the physical channel for data transfer. In the context of IEEE 802.15.4, the Data Link Layer includes the Media Access Control (MAC) layer, which facilitates channel access using carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance. The 802.15.4 MAC layer handles various functions, including network synchronization, time slot allocation, device association, and security services. While the IEEE 802.15.4 standard focuses on the Data Link Layer, higher network and application layers can interface with the protocol using convergence sublayers.
The correct answer is:
Data Link Layer
Explanation:
IEEE 802.15.4 primarily addresses the Data Link Layer of the OSI model, specifically focusing on:
- Media Access Control (MAC) Sub-Layer:
- Provides mechanisms for channel access using Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA).
- Manages tasks like network synchronization, time slot allocation, device association, and security.
- Logical Link Control (LLC) Sub-Layer:
- Interfaces with higher layers and ensures reliable data transfer.
While IEEE 802.15.4 focuses on the Data Link Layer, it also interacts with the Physical Layer, which it relies on for wireless transmission, and higher layers like the network and application layers via convergence sublayers. This standard is widely used in low-power, low-data-rate wireless networks, such as Zigbee and IoT applications.
13. Which topology in IEEE 802.15.4 wireless networks involves a single central controller, the PAN coordinator, and allows each network to operate independently by choosing a unique PAN identifier?
- Star Topology
- Cluster Tree Topology
- Peer-to-peer Topology
- Mesh Topology
In a star topology, communication is established between devices and a single central controller, known as the PAN coordinator. The PAN coordinator plays a crucial role; after activation, it may establish its own network. Each star network in this topology chooses a PAN identifier that no other network uses, allowing independent operation. This topology is suitable for applications such as home automation, wireless sensors, PC peripherals, toys, and games.
The correct answer is:
Star Topology
Explanation:
In Star Topology for IEEE 802.15.4 wireless networks:
- Central Controller: A single central device, called the PAN Coordinator, manages the network.
- Independent Operation: Each star network can operate independently by selecting a unique PAN identifier.
- Communication: All communication between devices is routed through the PAN Coordinator.
This topology is ideal for:
- Simple Networks: Home automation, wireless sensors, PC peripherals, toys, and games.
- Low-Power and Low-Complexity Applications: Star topology simplifies communication and reduces energy consumption for connected devices.
14. What is the purpose of a sink node in a WSN?
- It gathers and stores data from the environment.
- It receives data from the sensor nodes and forwards that data to a gateway for connection to external networks.
- It performs real-time monitoring of physical and conditions in the environment like temperature, moisture, vibration, pollution, or motion.
- It acts as an originator of data and sends the data to a router.
Once sensor nodes have collected data, they process the data and forward it wirelessly to other nodes until it reaches a sink node. The sink node receives data from the sensor nodes and forwards that data over a wired or wireless backbone to a gateway for connection to external networks or the Internet.
The correct answer is:
It receives data from the sensor nodes and forwards that data to a gateway for connection to external networks.
Explanation:
A sink node in a Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) plays a critical role by:
- Receiving Data: Collects data from multiple sensor nodes within the network.
- Forwarding Data: Sends the aggregated data to a gateway or external network, enabling further processing or integration with other systems.
- Communication Bridge: Acts as a bridge between the local WSN and external networks like the Internet.
The sink node is not responsible for originating or directly monitoring environmental conditions but facilitates the transfer of data collected by the sensor nodes to external systems for analysis or action.
15. Match the different WPANs to their common usage.
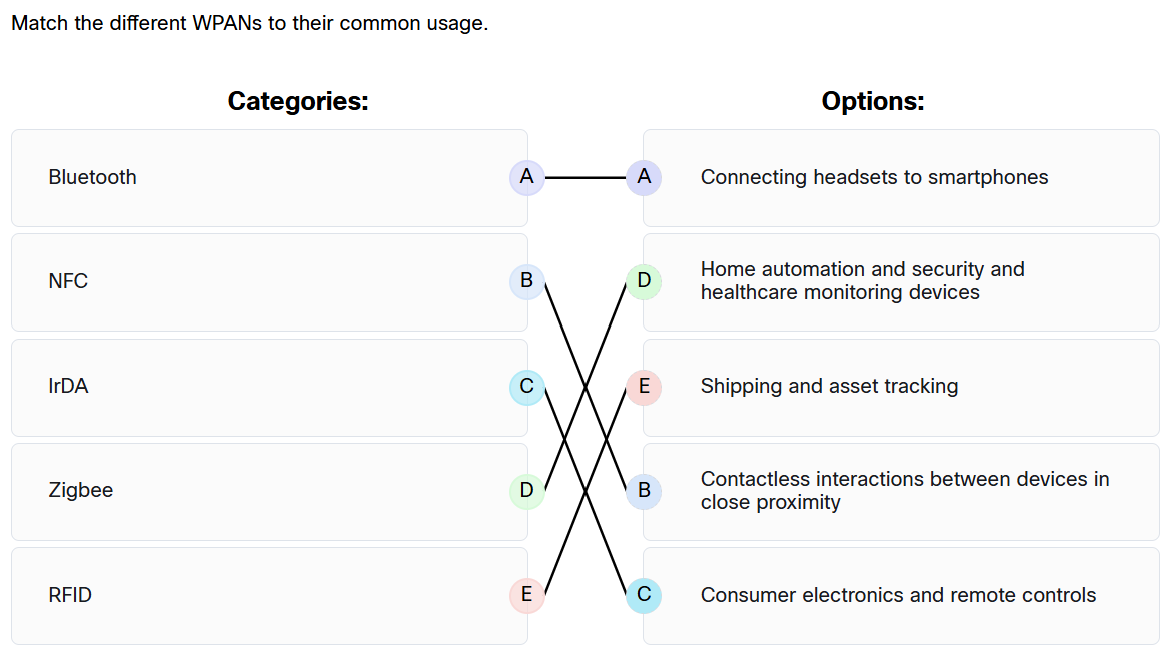
Here is the correct matching of the WPANs to their common usage:
- Bluetooth: Connecting headsets to smartphones
- NFC: Contactless interactions between devices in close proximity
- IrDA: Consumer electronics and remote controls
- Zigbee: Home automation, security, and healthcare monitoring devices
- RFID: Shipping and asset tracking